Open Projects
▶ VITRON
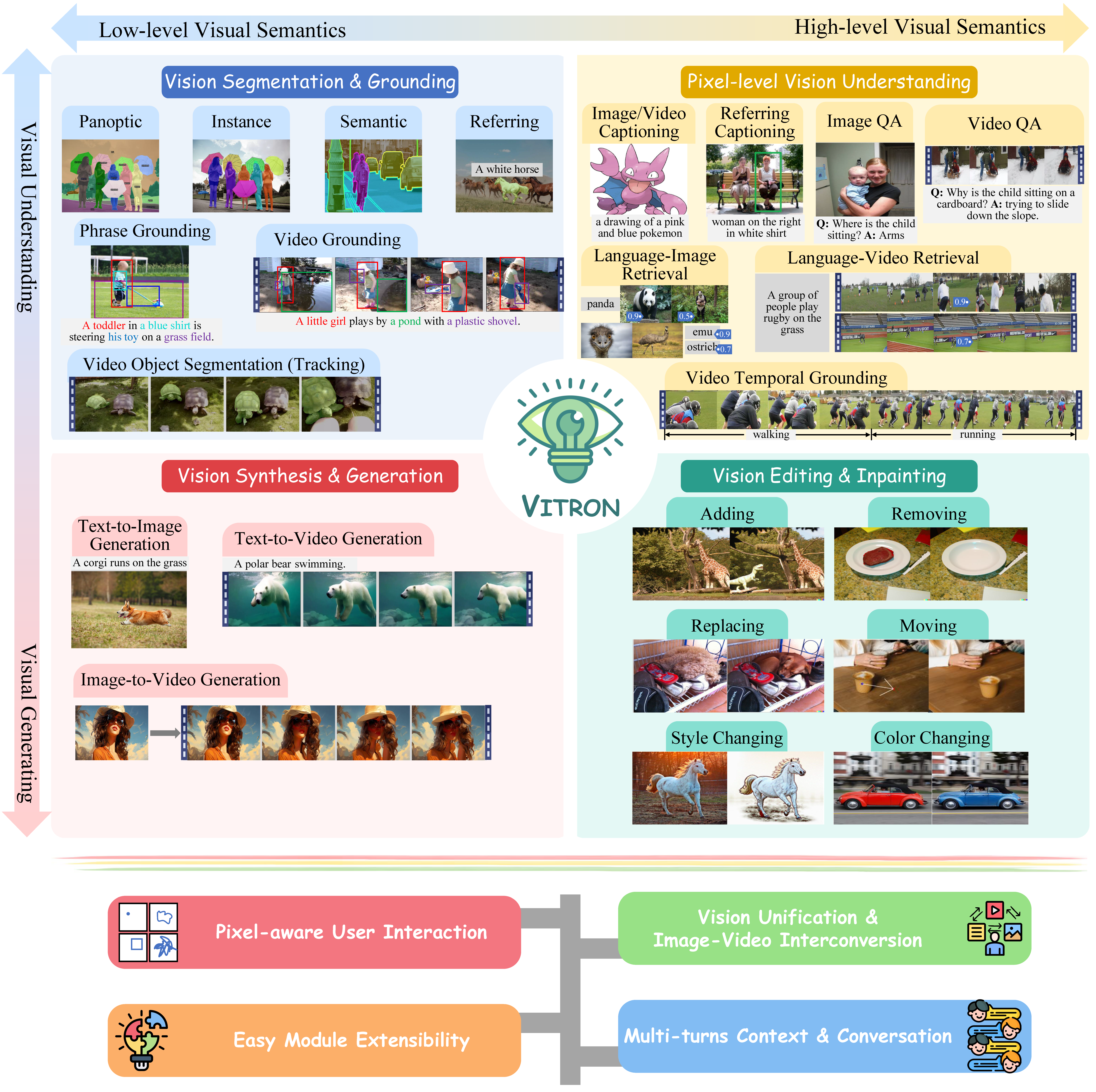
• VITRON: A Unified Pixel-level Vision LLM for Understanding, Generating, Segmenting, Editing
• Project site (with demo)
• Description: Recent developments of vision large language models (LLMs) have seen remarkable progress, yet still encounter challenges towards multimodal generalists, such as coarse-grained instance-level understanding, lack of unified support for both images and videos, and insufficient coverage across various vision tasks. To fill the gaps, we present Vitron, a universal pixel-level vision LLM designed for comprehensive understanding, generating, segmenting, and editing of both static image and dynamic video content. Utilizing an LLM backbone, Vitron incorporates specialized encoders for images, videos, and pixel-level regional visuals within its frontend architecture, while as its backend, employing a text-centric invocation strategy for integrating diverse state-of-the-art off-the-shelf modules tailored for an array of vision-related end tasks. Via this, Vitron supports a spectrum of vision end tasks, spanning visual understanding to visual generation, from low level to high level. Through joint vision-language alignment and fine-grained region-aware instruction tuning, Vitron achieves precise pixel-level perception. We further enhance its capabilities with invocation-oriented instruction tuning, allowing for flexible and precise module invocation for downstream vision tasks. Demonstrated over 12 visual tasks and evaluated across 22 datasets, Vitron showcases its extensive capabilities in the four main vision task clusters, e.g., segmentation, understanding, content generation, and editing. Various demonstrations also illustrate Vitron’s fortes in visual manipulation and user interactivity. Overall, this work illuminates the great potential of developing a more unified and interactive visual multimodal generalist, setting new frontiers for the next vision research.
▶ NExT-GPT
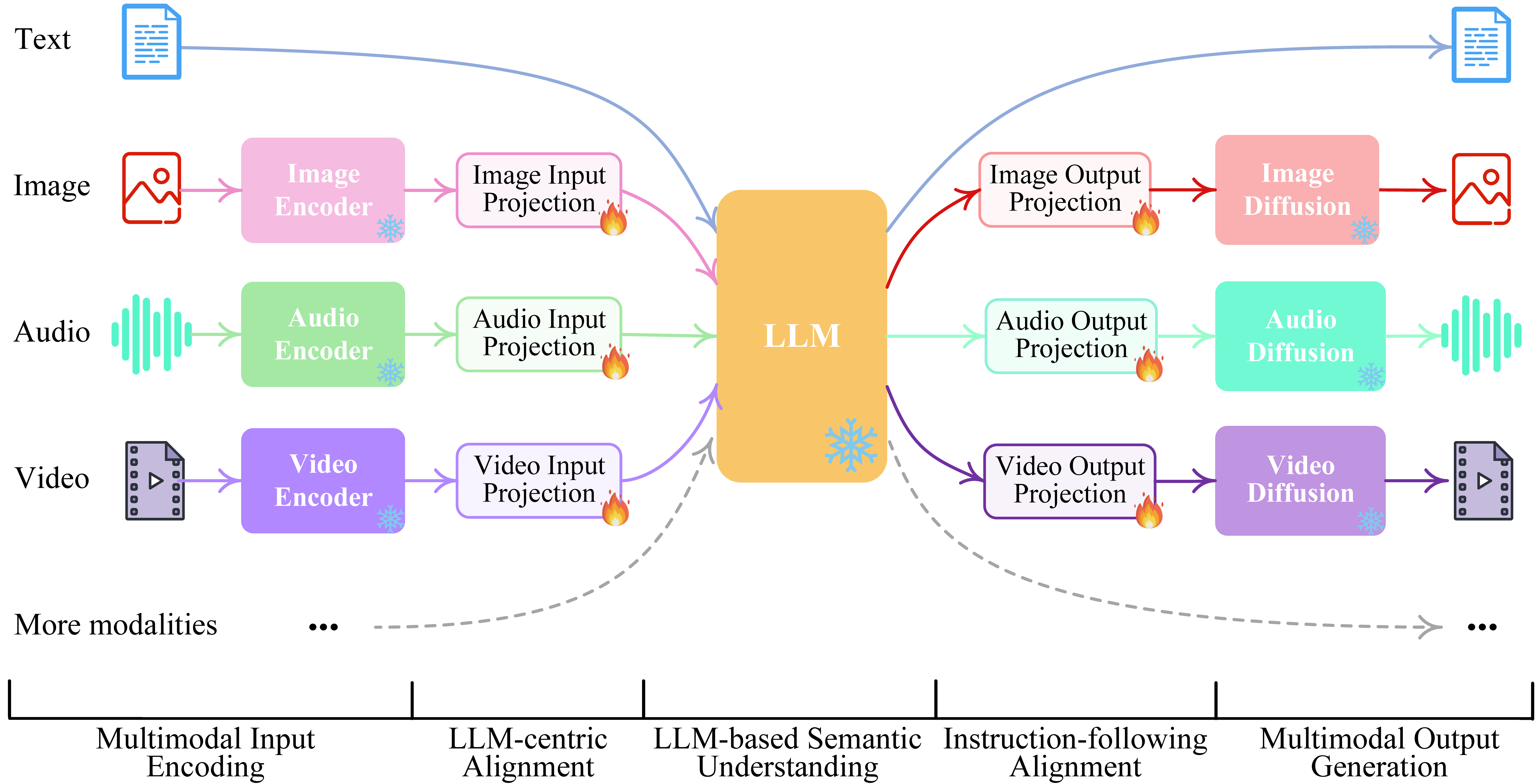
• NExT-GPT: Any-to-Any Multimodal Large Language Model
• Project site (with demo)
• Description: While recently Multimodal Large Language Models (MM-LLMs) have made exciting strides, they mostly fall prey to the limitation of only input-side multimodal understanding, without the ability to produce content in multiple modalities. As we humans always perceive the world and communicate with people through various modalities, developing any-to-any MM-LLMs capable of accepting and delivering content in any modality becomes essential to human-level AI. To fill the gap, we present an end-to-end general-purpose any-to-any MM-LLM system, NExT-GPT. We connect an LLM with multimodal adaptors and different diffusion decoders, enabling NExT-GPT to perceive inputs and generate outputs in arbitrary combinations of text, images, videos, and audio. By leveraging the existing well-trained highly-performing encoders and decoders, NExT-GPT is tuned with only a small amount of parameter (1%) of certain projection layers, which not only benefits low-cost training and also facilitates convenient expansion to more potential modalities. Moreover, we introduce a modality-switching instruction tuning (MosIT) and manually curate a high-quality dataset for MosIT, based on which NExT-GPT is empowered with complex cross-modal semantic understanding and content generation. Overall, our research showcases the promising possibility of building an AI agent capable of modeling universal modalities, paving the way for more human-like AI research in the community.
▶ Dysen-VDM
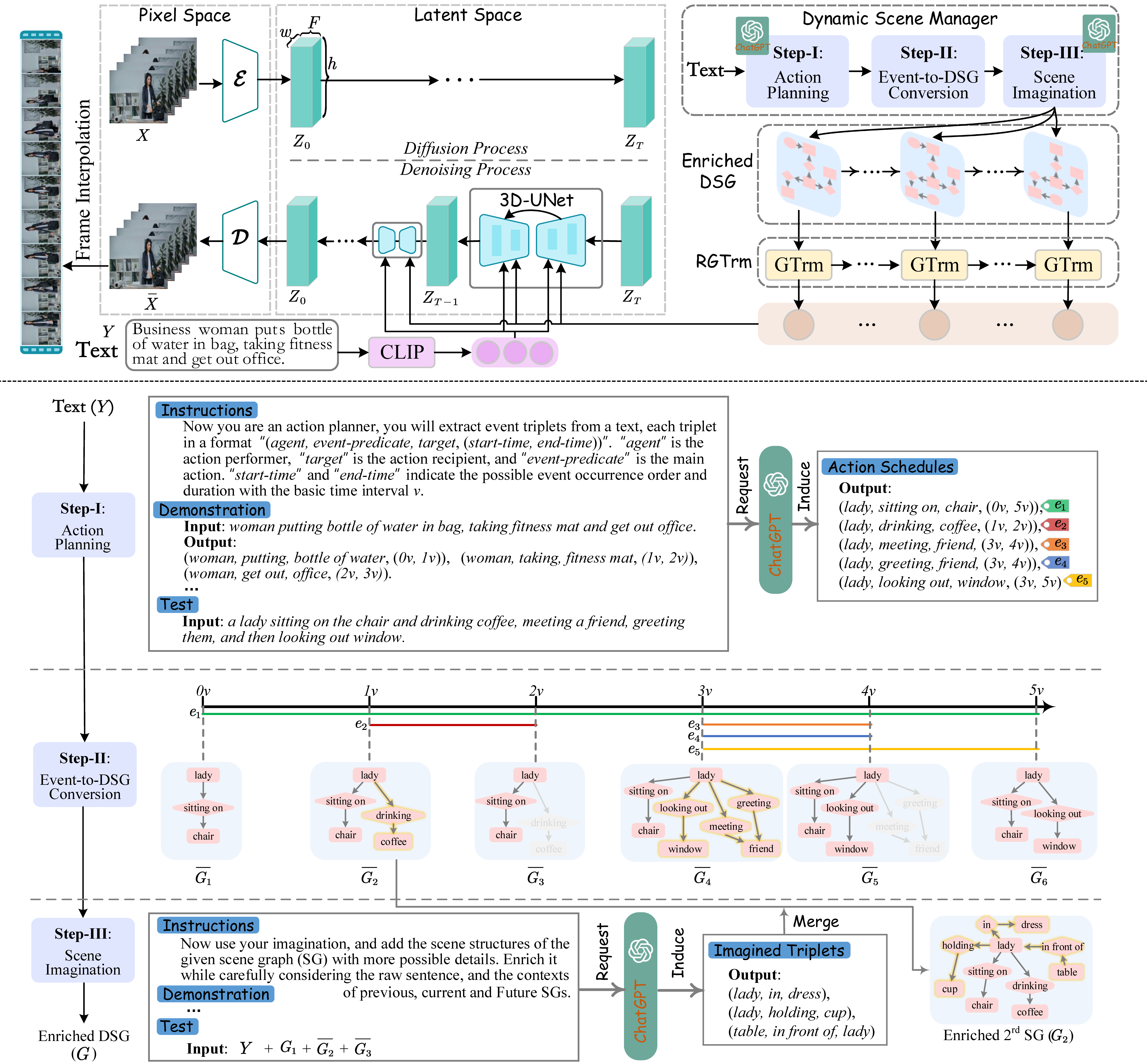
• Dysen-VDM: Empowering Dynamics-aware Text-to-Video Diffusion with Large Language Models
• Project site (with demo)
• Description: Text-to-video (T2V) synthesis has gained increasing attention in the community, in which the recently emerged diffusion models (DMs) have promisingly shown stronger performance than the past approaches. While existing state-of-the-art (SoTA) DMs are competent to achieve high-resolution video generation, they may largely suffer from key limitations (e.g., action occurrence disorders, crude video motions) with respect to the intricate temporal dynamics modeling, one of the crux of video synthesis. In this work, we investigate strengthening the awareness of video dynamics for DMs, for high-quality T2V generation. Inspired by human intuition, we design an innovative dynamic scene manager (dubbed as Dysen) module, which includes (step-1) extracting from input text the key actions with proper time-order arrangement, (step-2) transforming the action schedules into the dynamic scene graph (DSG) representations, and (step-3) enriching the scenes in the DSG with sufficient and reasonable details. Taking advantage of the existing powerful LLMs (e.g., ChatGPT) via in-context learning, Dysen realizes (nearly) human-level temporal dynamics understanding. Finally, the resulting video DSG with rich action scene details is encoded as fine-grained spatio-temporal features, integrated into the backbone T2V DM for video generating. Experiments on popular T2V datasets suggest that our framework consistently outperforms prior arts with significant margins, especially in the scenario with complex actions.
▶ LayoutLLM-T2I
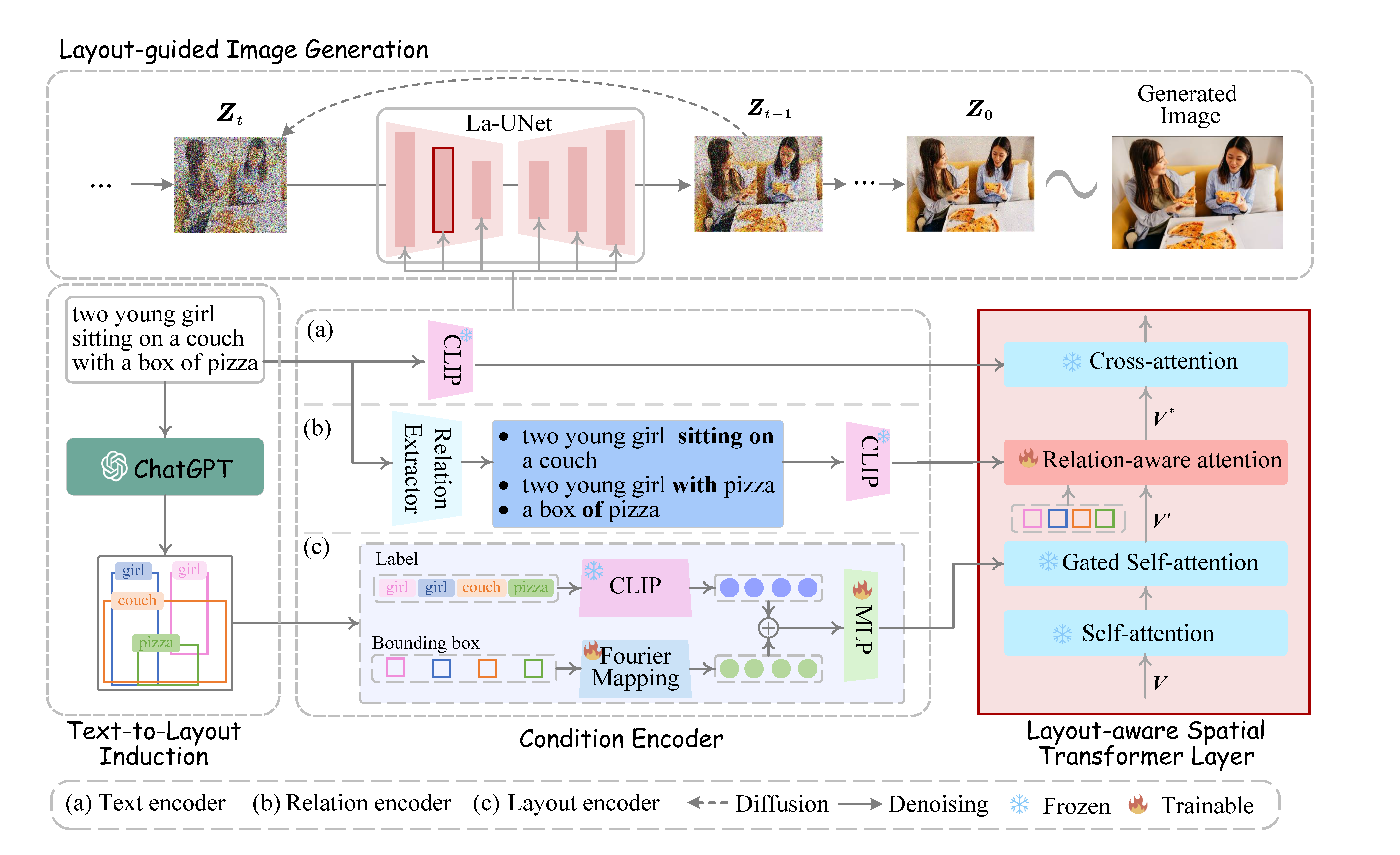
• LayoutLLM-T2I: Eliciting Layout Guidance from LLM for Text-to-Image Generation
• Project site (with demo)
• Description: In the text-to-image generation field, recent remarkable progress in Stable Diffusion makes it possible to generate rich kinds of novel photorealistic images. However, current models still face misalignment issues (e.g., problematic spatial relation understanding and numeration failure) in complex natural scenes, which impedes the high-faithfulness text-to-image generation. Although recent efforts have been made to improve controllability by giving fine-grained guidance (e.g., sketch and scribbles), this issue has not been fundamentally tackled since users have to provide such guidance information manually. In this work, we strive to synthesize high-fidelity images that are semantically aligned with a given textual prompt without any guidance. Toward this end, we propose a coarse-to-fine paradigm to achieve layout planning and image generation. Concretely, we first generate the coarse-grained layout conditioned on a given textual prompt via in-context learning based on Large Language Models. Afterward, we propose a fine-grained object-interaction diffusion method to synthesize high-faithfulness images conditioned on the prompt and the automatically generated layout. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art models in terms of cross-modal text-layout alignment and high-faithfulness image generation.
▶ XNLP
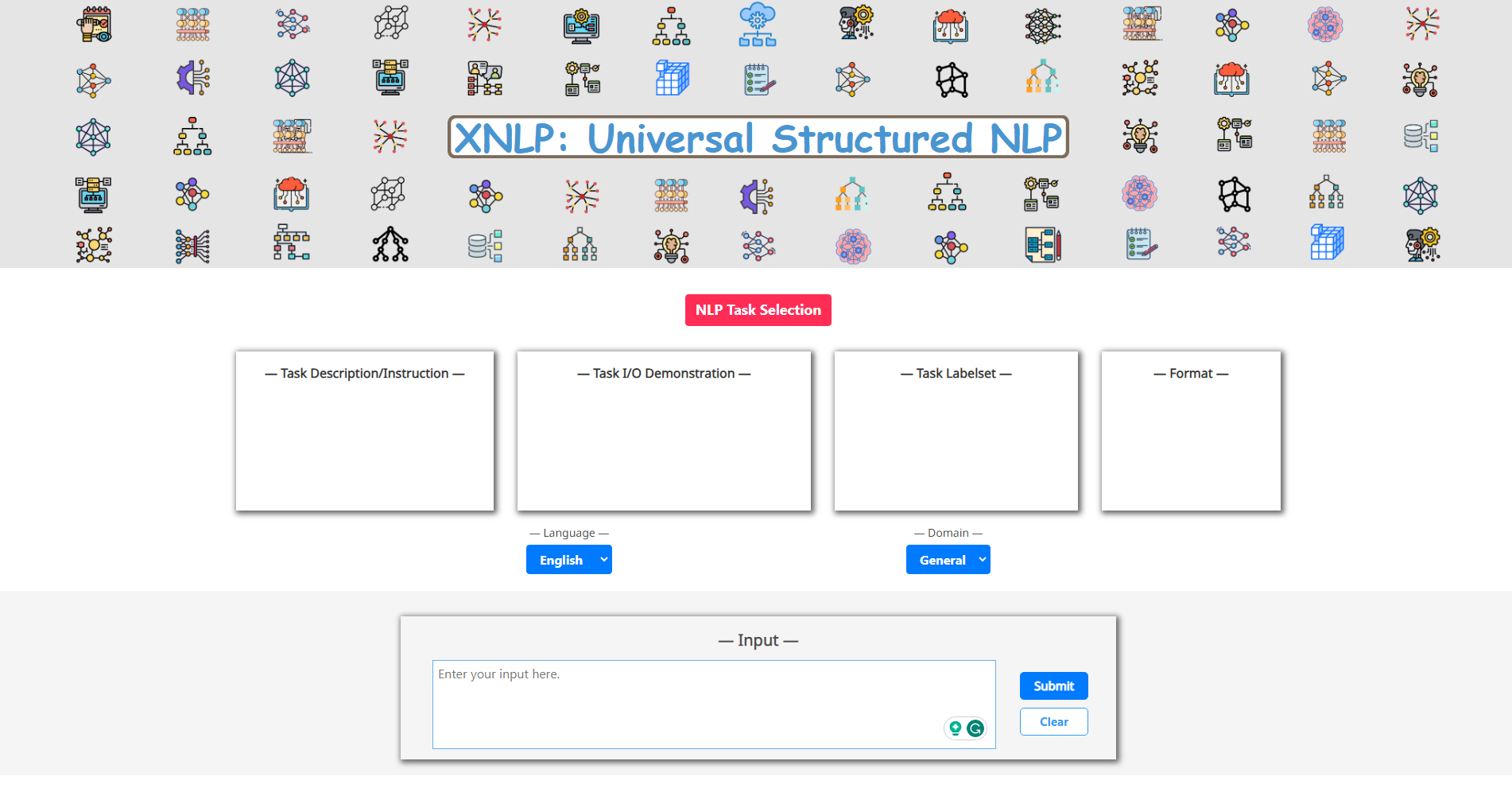
• XNLP: An Interactive Demonstration System for Universal Structured NLP
• Project site (with demo)
• Description: Structured Natural Language Processing (XNLP) is an important subset of NLP that entails understanding the underlying semantic or syntactic structure of texts, which serves as a foundational component for many downstream applications. Despite certain recent efforts to explore universal solutions for specific categories of XNLP tasks, a comprehensive and effective approach for unifying all XNLP tasks long remains underdeveloped. In the meanwhile, while XNLP demonstration systems are vital for researchers exploring various XNLP tasks, existing platforms can be limited to, e.g., supporting few XNLP tasks, lacking interactivity and universalness. To this end, we propose an advanced XNLP demonstration platform, where we propose leveraging LLM to achieve universal XNLP, with one model for all with high generalizability. Overall, our system advances in multiple aspects, including universal XNLP modeling, high performance, interpretability, scalability, and interactivity, providing a unified platform for exploring diverse XNLP tasks in the community.
▶ VPGTrans
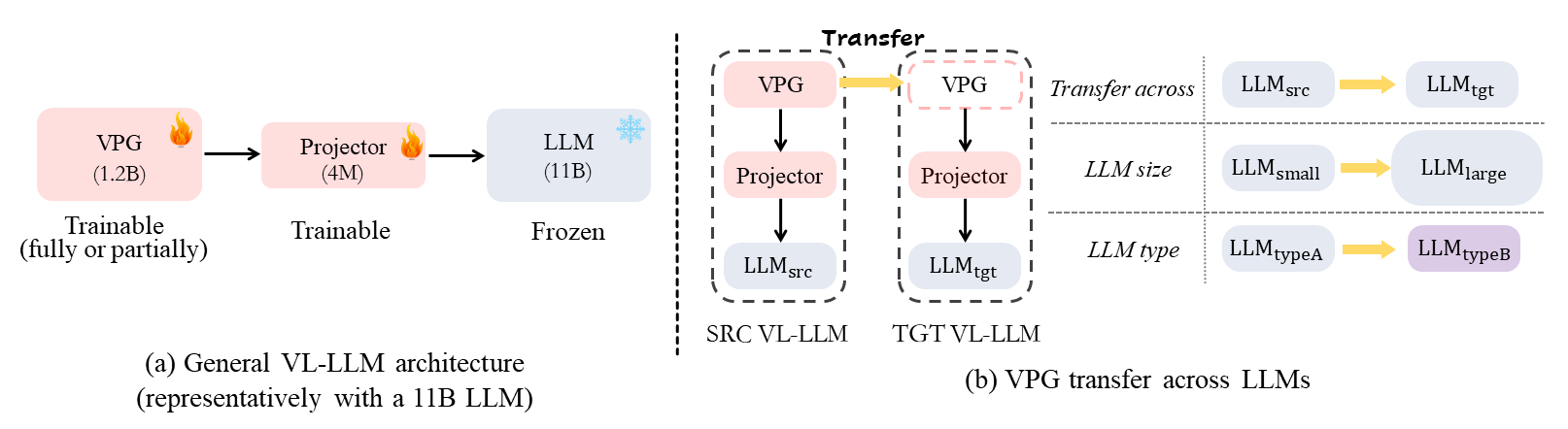
• VPGTrans: Transfer Visual Prompt Generator across LLMs
• Project site (with demo)
• Description: While developing a new vision-language LLM (VL-LLM) by pre-training on tremendous image-text pairs from scratch can be exceedingly resource-consuming, connecting an existing LLM with a comparatively lightweight visual prompt generator (VPG) becomes a feasible paradigm. However, further tuning the VPG part of the VL-LLM still suffers from indispensable computational costs, i.e., requiring thousands of GPU hours and millions of training data. One alternative solution is to transfer an existing VPG from any existing VL-LLMs for the target VL-LLM. In this work, we for the first time investigate the VPG transferability across LLMs, and explore a solution to reduce the cost of VPG transfer. We first study the VPG transfer across different LLM sizes (e.g., small-to-large), and across different LLM types, through which we diagnose the key factors to maximize the transfer efficiency. Based on our observation, we design a two-stage transfer framework named VPGTrans, which is simple yet highly effective. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that VPGTrans helps significantly speed up the transfer learning process without compromising performance. Remarkably, it helps achieve the VPG transfer from BLIP-2 OPT2.7B to BLIP-2 OPT6.7B with over 10 times speed-up and 10.7% training data compared with connecting a VPG to OPT6.7B from scratch. Further, a series of intriguing findings and potential rationales behind them are provided and discussed. Finally, we showcase the application value of our VPGTrans approach, by newly customizing two novel VL-LLMs, including VL-LLaMA and VL-Vicuna, with recently released LLaMA and Vicuna models. With our VPGTrans, one can build a novel high-performance VL-LLM based on any existing text-based LLMs and an existing VPG with considerably lower cost.
▶ BiLSTM+CRF
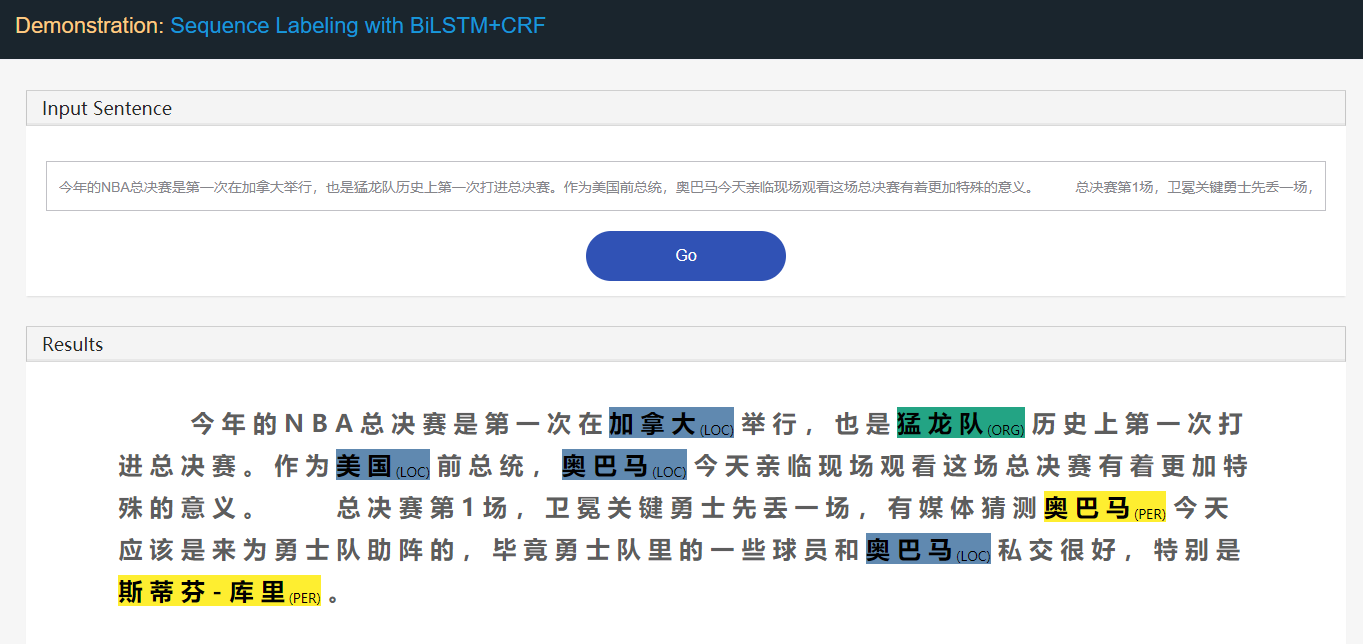
• BiLSTM+CRF system for Sequential Labeling Tasks
• Project site (with demo)
• Description: A TensorFlow implementation of BiLSTM+CRF model, for NLP sequence labeling tasks. Sequential labeling is one typical methodology modeling the sequence prediction tasks in NLP. Common sequential labeling tasks include, e.g., Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging, Chunking, Named Entity Recognition (NER), Sentence Boundary Detection, Chinese Word Segmentation (CWG), Semantic Role Labeling (SRL), Event Extraction, and so forth. This TensforFlow-based BiLSTM+CRF system advances in highly scalable; everything is configurable; modularized with clear structure; very friendly for beginners and easy to DIY.
▶ THOR

• Reasoning Implicit Sentiment with Chain-of-Thought Prompting
• Project site
• Description: While sentiment analysis systems try to determine the sentiment polarities of given targets based on the key opinion expressions in input texts, in implicit sentiment analysis (ISA) the opinion cues come in an implicit and obscure manner. Thus detecting implicit sentiment requires the common-sense and multi-hop reasoning ability to infer the latent intent of opinion. Inspired by the recent chain-of-thought (CoT) idea, in this work we introduce a Three-hop Reasoning (THOR) CoT framework to mimic the human-like reasoning process for ISA. We design a three-step prompting principle for THOR to step-by-step induce the implicit aspect, opinion, and finally the sentiment polarity. Our THOR+Flan-T5 (11B) pushes the state-of-the-art (SoTA) by over 6% F1 on supervised setup. More strikingly, THOR+GPT3 (175B) boosts the SoTA by over 50% F1 on zero-shot setting.
▶ DiaASQ
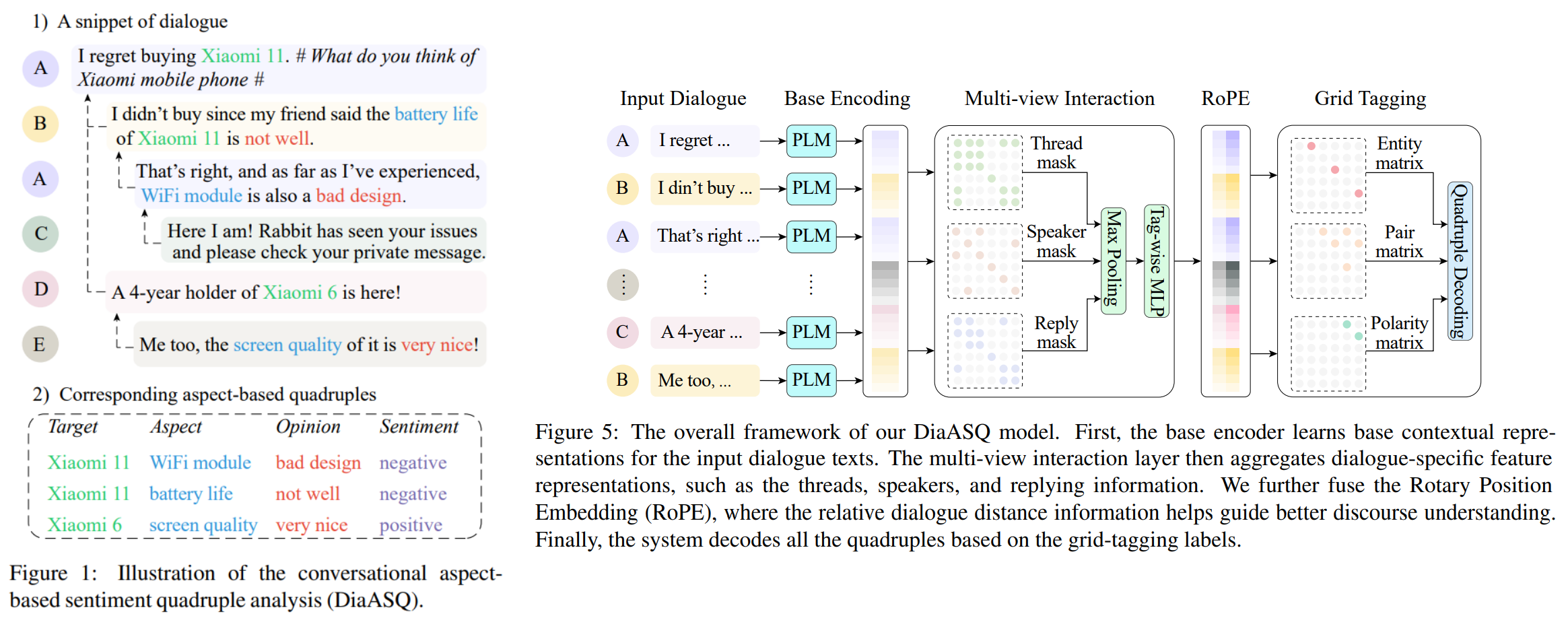
• DiaASQ: A Benchmark of Conversational Aspect-based Sentiment Quadruple Analysis
• Project site
• Description: The rapid development of aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) within recent decades shows great potential for real-world society. The current ABSA works, however, are mostly limited to the scenario of a single text piece, leaving the study in dialogue contexts unexplored. To bridge the gap between fine-grained sentiment analysis and conversational opinion mining, in this work, we introduce a novel task of conversational aspect-based sentiment quadruple analysis, namely DiaASQ, aiming to detect the quadruple of target-aspect-opinion-sentiment in a dialogue. We manually construct a large-scale high-quality DiaASQ dataset in both Chinese and English languages. We deliberately develop a neural model to benchmark the task, which advances in effectively performing end-to-end quadruple prediction, and manages to incorporate rich dialogue-specific and discourse feature representations for better cross-utterance quadruple extraction. We hope the new benchmark will spur more advancements in the sentiment analysis community.
▶ W2NER
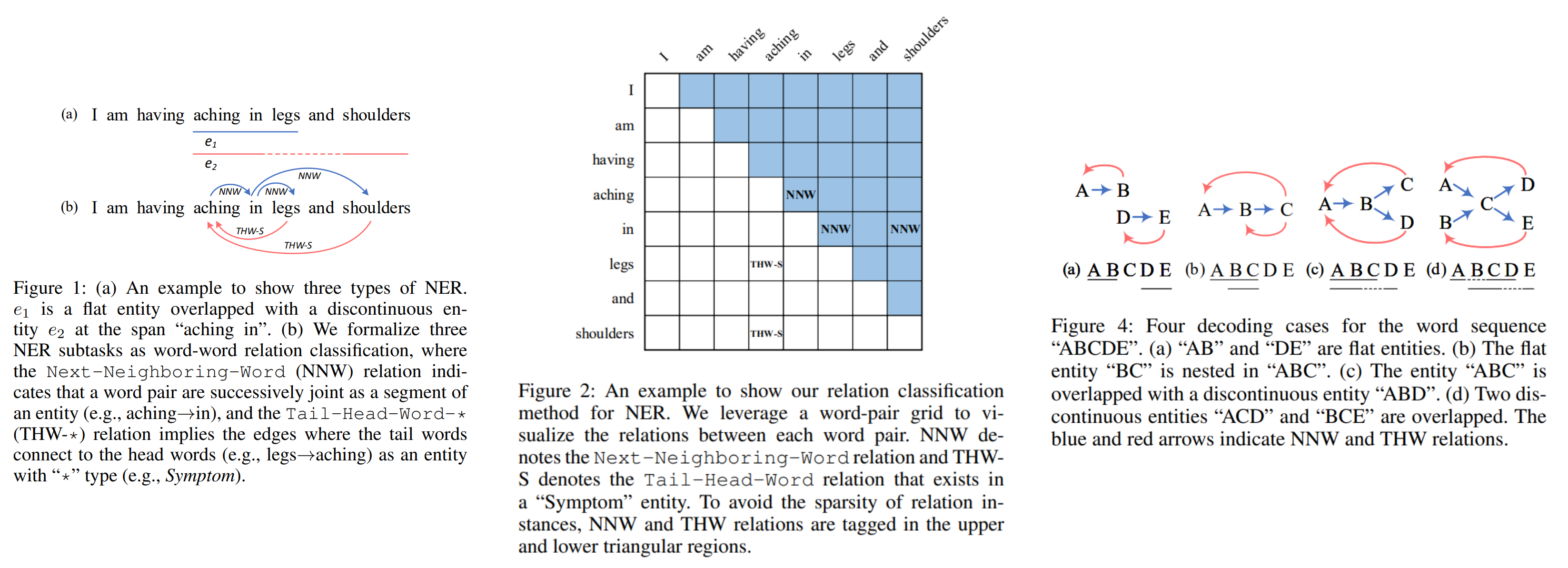
• Unified Named Entity Recognition as Word-Word Relation Classification
• Project site
• Description: We present a novel end-to-end NER (including flat, nested, discontinuous NER) system with a word-word relation classification modeling, named W2NER. The architecture resolves the kernel bottleneck of unified NER by effectively modeling the neighboring relations between entity words with Next-Neighboring-Word (NNW) and Tail-Head-Word-* (THW-*) relations. With the W2NER scheme, the unified NER can be modeled as a 2D grid of word pairs.
▶ LasUIE
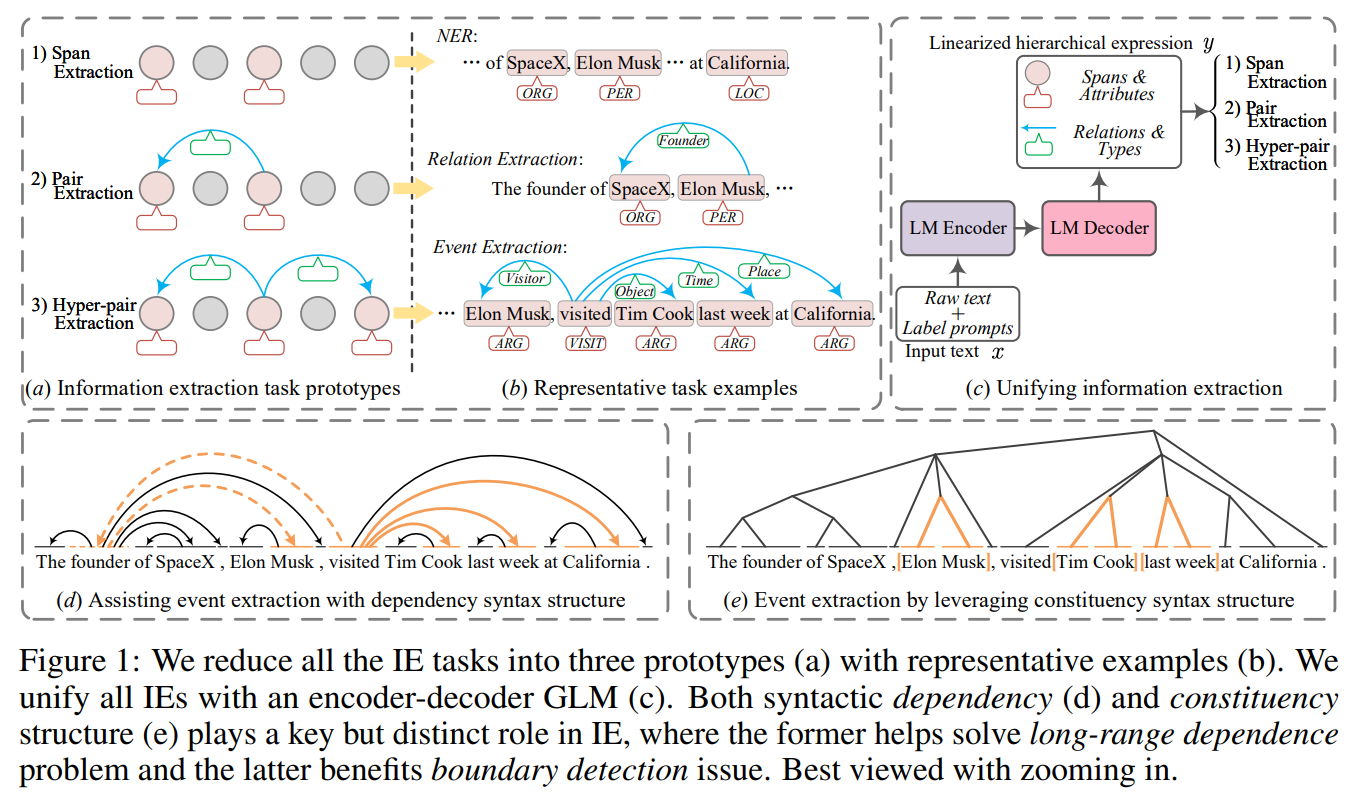
• LasUIE: Unifying Information Extraction with Latent Adaptive Structure-aware Generative Language Model
• Project site
• Description: Universally modeling all typical information extraction tasks (UIE) with one generative language model (GLM) has revealed great potential by the latest study, where various IE predictions are unified into a linearized hierarchical expression under a GLM. Syntactic structure information, a type of effective feature which has been extensively utilized in IE community, should also be beneficial to UIE. In this work, we propose a novel structure-aware GLM, fully unleashing the power of syntactic knowledge for UIE. A heterogeneous structure inductor is explored to unsupervisedly induce rich heterogeneous structural representations by post-training an existing GLM. In particular, a structural broadcaster is devised to compact various latent trees into explicit high-order forests, helping to guide a better generation during decoding. We finally introduce a task-oriented structure fine-tuning mechanism, further adjusting the learned structures to most coincide with the end-task’s need. Over 12 IE benchmarks across 7 tasks our system shows significant improvements over the baseline UIE system. Further in-depth analyses show that our GLM learns rich task-adaptive structural bias that greatly resolves the UIE crux, the long-range dependence issue and boundary identifying.
▶ SMDL
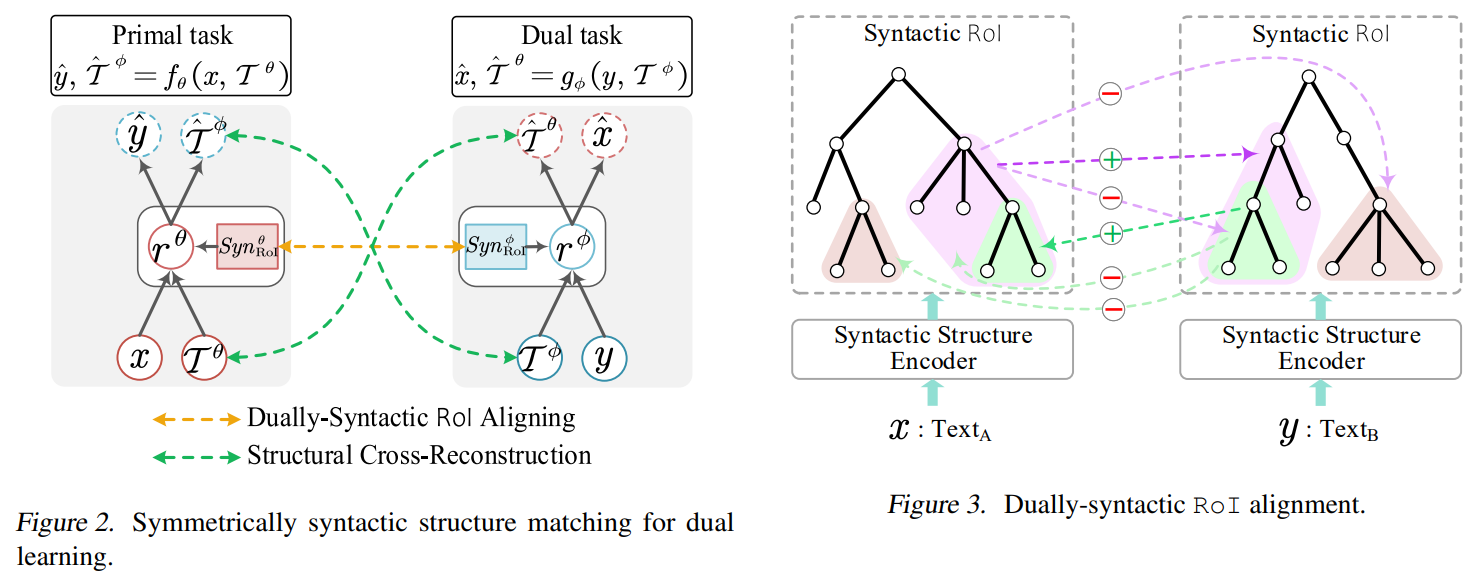
• Matching Structure for Dual Learning
• Project site
• Description: Many natural language processing (NLP) tasks appear in dual forms, which are generally solved by dual learning technique that models the dualities between the coupled tasks. In this work, we propose to further enhance dual learning with structure matching that explicitly builds structural connections in between. Starting with the dual text↔text generation, we perform duallysyntactic structure co-echoing of the region of interest (RoI) between the task pair, together with a syntax cross-reconstruction at the decoding side. We next extend the idea to a text↔non-text setup, making alignment between the syntactic-semantic structure. Over 2*14 tasks covering 5 dual learning scenarios, the proposed structure matching method shows its significant effectiveness in enhancing existing dual learning. Our method can retrieve the key RoIs that are highly crucial to the task performance. Besides NLP tasks, it is also revealed that our approach has great potential in facilitating more non-text↔non-text scenarios.
▶ UABSA
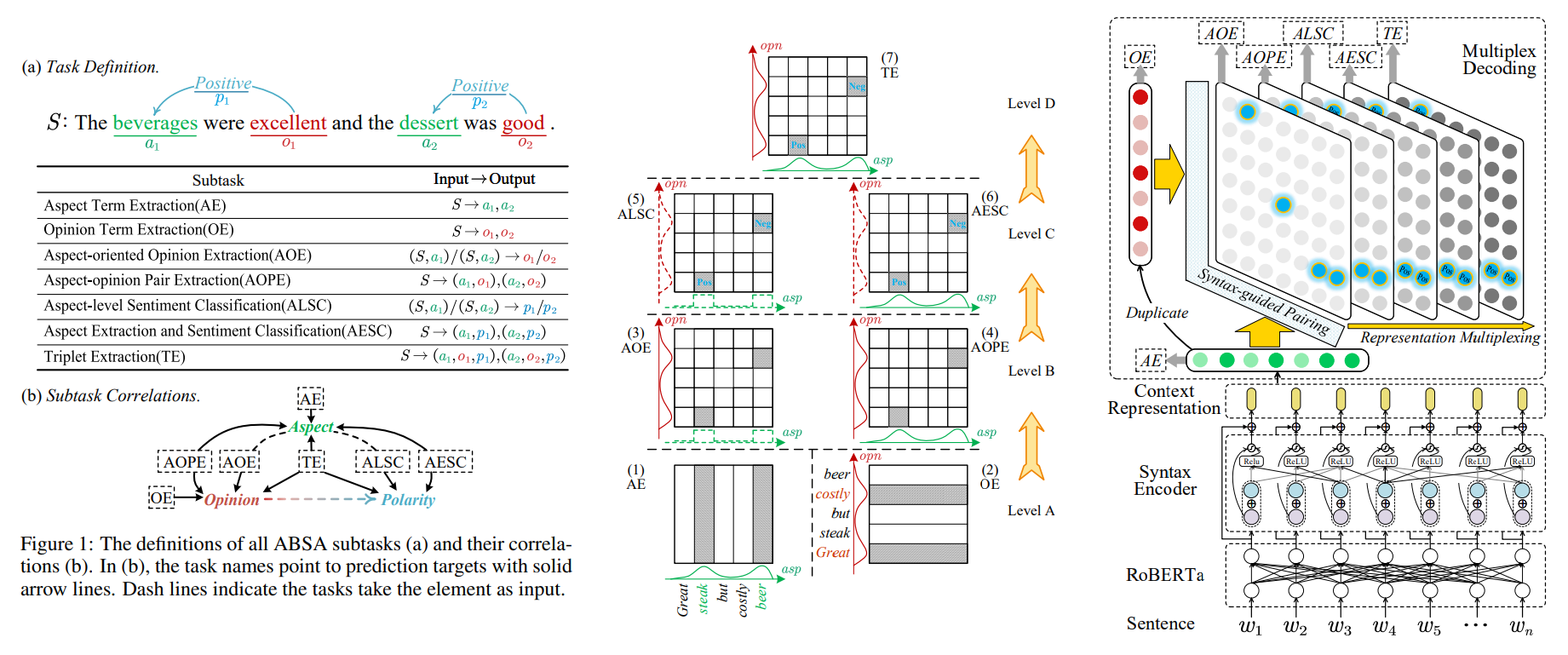
• Inheriting the Wisdom of Predecessors: A Multiplex Cascade Framework for Unified Aspect-based Sentiment Analysis
• Project site
• Description: So far, aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA) has involved with total seven subtasks, in which, however the interactions among them have been left unexplored sufficiently. This work presents a novel multiplex cascade framework for unified ABSA and maintaining such interactions. First, we model total seven subtasks as a hierarchical dependency in the easy-to-hard order, based on which we then propose a multiplex decoding mechanism, transferring the sentiment layouts and clues in lower tasks to upper ones. The multiplex strategy enables highly-efficient subtask interflows and avoids repetitive training; meanwhile it sufficiently utilizes the existing data without requiring any further annotation. Further, based on the characteristics of aspect-opinion term extraction and pairing, we enhance our multiplex framework by integrating POS tag and syntactic dependency information for term boundary and pairing identification. The proposed Syntax-aware Multiplex (SyMux) framework enhances the ABSA performances on 28 subtasks (7×4 datasets) with big margins.
▶ XSRL
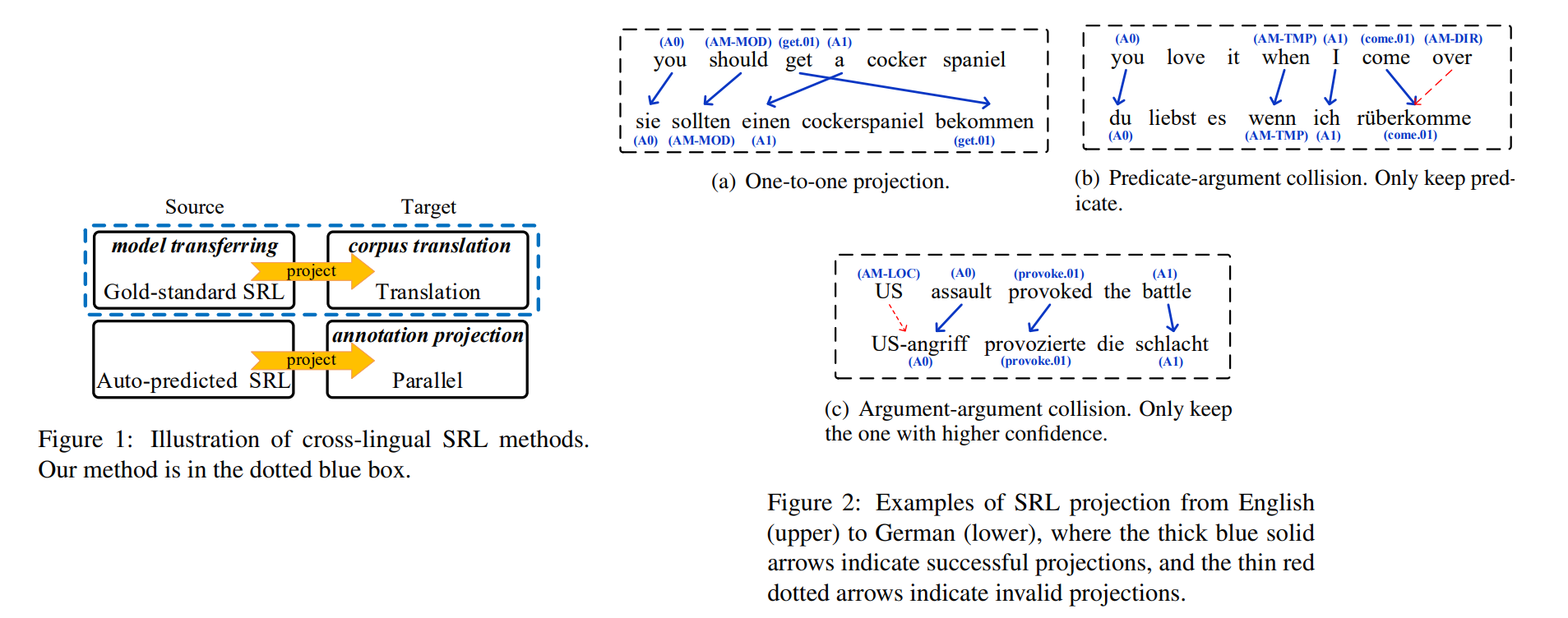
• Cross-Lingual Semantic Role Labeling with High-Quality Translated Training Corpus
• Project site
• Description: Many efforts of research are devoted to semantic role labeling (SRL) which is crucial for natural language understanding. Supervised approaches have achieved impressing performances when large-scale corpora are available for resource-rich languages such as English. While for the low-resource languages with no annotated SRL dataset, it is still challenging to obtain competitive performances. Cross-lingual SRL is one promising way to address the problem, which has achieved great advances with the help of model transferring and annotation projection. In this paper, we propose a novel alternative based on corpus translation, constructing high-quality training datasets for the target languages from the source gold-standard SRL annotations. Experimental results on Universal Proposition Bank show that the translation-based method is highly effective, and the automatic pseudo datasets can improve the target-language SRL performances significantly.
▶ HeSyFu
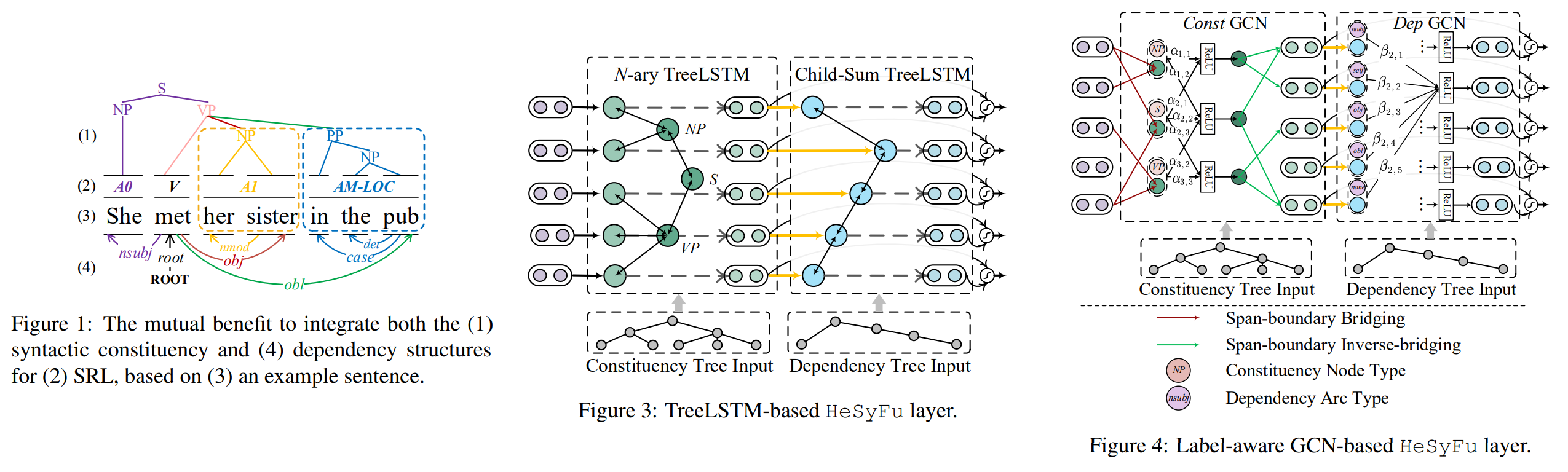
• Better Combine Them Together! Integrating Syntactic Constituency and Dependency Representations for Semantic Role Labeling
• Project site
• Description: Structural syntax knowledge has been proven effective for semantic role labeling (SRL), while existing works mostly use only one singleton syntax, such as either syntactic dependency or constituency tree. In this project, we explore the integration of heterogeneous syntactic representations for SRL. We first consider a TreeLSTM-based integration, collaboratively learning the phrasal boundaries from the constituency and the semantic relations from dependency. We further introduce a label-aware GCN solution for simultaneously modeling the syntactic edges and labels. Experimental results demonstrate that by effectively combining the heterogeneous syntactic representations, our methods yield task improvements on both span-based and dependencybased SRL. Also our system achieves new state-of-the-art SRL performances, meanwhile bringing explainable task improvements.